
Klimafloor
Project focus
- Development of an automated robot for the leveling of pour-in insulation
- Evaluation of different control strategies
- Vision-based path planning for obstacle avoidance and optimal distribution of the material
Description
The project deals with the total installation and processing of floor structures including underfloor heating of our industrial partner mixit Dämmstoffe GmbH. In the field of house constructions, the leveling of screed or pour-in insulation is considered an exhausting and harmful task for the construction workers. In order to overcome these issues, our focus in the project lies on the construction of an automated leveling robot in order to increase the distribution quality and achieve a shorter processing time. The robot system consists of several modular components, which allows fast and easy transportation and assembly. To ensure that the working tool stays level, a rotational laser is set up as guidance. In order to avoid contact with obstacles, e.g. walls, distance sensors and a 3D camera are used.
Automation and control of the leveling platform
As a first prototype, an existing platform was used as a starting point. This platform has a SCARA-like structure with a two-linked arm mounted on a foldable tripod and uses a projected laser line to automatically adjust the tool height, while the rest of the system is operated manually. As the base has to be leveled during each new set-up, automation of this process saves a considerable amount of time. In order to facilitate this, two servomotors were mounted on the height-setting screws on the legs and a tilt sensor was added to provide the measurements needed for feedback control. The automatic leveling also allows us to accurately estimate the leg positions without direct measurement, which is later useful during the path planning phase.

Automated robot platform for the leveling of pour-in insulation
For the movement of the arm itself, larger synchronous servomotors were added to each of the three joints in a belt drive configuration. Through inverse kinematics and dynamics, these actuators allow precise control over the end-effector position. Motor torque is also measured and will enable us to use more advanced control strategies, such as impedance control, avoiding potentially harmful hard contact with obstacles.
A novel laser line detector is developed to provide the needed accuracy. With the aim of better suit the intended task, new designs for the robot tool are developed and tested in a construction site environment.
Vision-based obstacle detection and path planning
For the detection of the walls in the 3D point cloud, the Sequential RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) algorithm is used. In future evaluations, also algorithms such as MultiRANSAC or Residual Histogram Analysis can be tested.
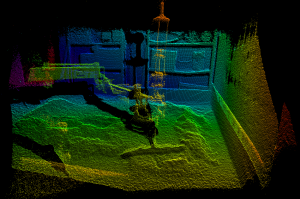
Point cloud of robot during leveling process
The first step in the vision-based path planning is to obtain the knowledge of the to be processed plane. This is done by detecting the laser line of the rotational laser. With the camera mounted on top of the robot, the plane can be calculated. Subsequently, areas with too much or too less material can be perceived.
Related publications
- M. Bibl, R. Stein, E. Döberl, and G. Schitter, Rotierender optischer Positions- und Winkelsensor, E&I Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik, vol. 135, iss. 6, p. 396–400, 2018.
[BibTex]@Article{TUW-272096, author = {Bibl, Matthias and Stein, Robert and D{\"o}berl, Egon and Schitter, Georg}, title = {Rotierender optischer Positions- und Winkelsensor}, journal = {E{\&}I Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik}, year = {2018}, volume = {135}, number = {6}, pages = {396--400}, keywords = {Positions- und Winkelmessung, Rotierender optischer Sensor, Optische Messtechnik}, doi = {10.1007/s00502-018-0642-3} }
- M. Hurban, M. Melik-Merkumians, M. Steinegger, M. Bibl, P. Gsellmann, and G. Schitter, Automated Tripod Leveling and Parameter Estimation for a Granular-fill Insulation Distributing Robot, in Proceedings of the Joint Conference 8th IFAC Symposium on Mechatronic Systems (MECHATRONICS 2019), and 11th IFAC Symposium on Nonlinear Control Systems (NOLCOS 2019), 2019.
[BibTex] [Download]@InProceedings{TUW-282489, author = {Hurban, Milan and Melik-Merkumians, Martin and Steinegger, Michael and Bibl, Matthias and Gsellmann, Peter and Schitter, Georg}, title = {Automated Tripod Leveling and Parameter Estimation for a Granular-fill Insulation Distributing Robot}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the Joint Conference 8th IFAC Symposium on Mechatronic Systems (MECHATRONICS 2019), and 11th IFAC Symposium on Nonlinear Control Systems (NOLCOS 2019)}, year = {2019}, volume = {52/15}, note = {Vortrag: Joint Conference 8th IFAC Symposium on Mechatronic Systems (MECHATRONICS 2019), and 11th IFAC Symposium on Nonlinear Control Systems (NOLCOS 2019), Wien; 2019-09-04 -- 2019-09-06}, doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.11.678}, journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine/Elsevier}, keywords = {Robotic manipulators, Linearization, Kalman Filters, Parameter estimation, LQG control method}, numpages = {6}, }
Project partners
Funding
Contact
Univ.-Prof. Dipl.-Ing. Dr.sc.techn. Georg SchitterDipl.-Ing. Martin Melik-Merkumians
Project Staff
Dipl.-Ing. Martin Melik-MerkumiansDipl.-Ing. BSc. Peter Gsellmann
Ing. MSc. Milan Hurban
Dipl.-Ing. Matthias Bibl
Michael Weidinger, BSc
Tobias Steinegger