Versatile technology platform for MEMS scan system for automotive safety applications (AUTOScan)
Project focus
- Versatile technology for automotive MEMS mirror
- Sensing and Actuation for high performance MEMS scan systems
- Advanced control development for automotive qualified MEMS scan systems
- Feasibility evaluation of the MEMS scan system for automotive safety applications.
Description
Advancements of sensors, communication and artificial intelligence are about to bring a revolutionary changes in mobility and transportation by autonomous driving. Scanning mirrors based on Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) technologies are one of the promising solutions for various automotive applications, e.g. photonic sensing such as lidars and human machine interfaces such as augmented reality head -up display (AR HUD) and smart headlights. Small form factor, high scanning performance and scalable low unit cost by mass production are raised as main advantages of the MEMS scanning solution for automotive applications. As a drawback, MEMS mirrors are prone to harsh operating conditions such as vibrations, shocks, and temperature variations, requiring highly robust system design with controls to guarantee their full device performance at any situation. However, it is challenging for analysis and control design since MEMS mirrors are highly nonlinear devices.
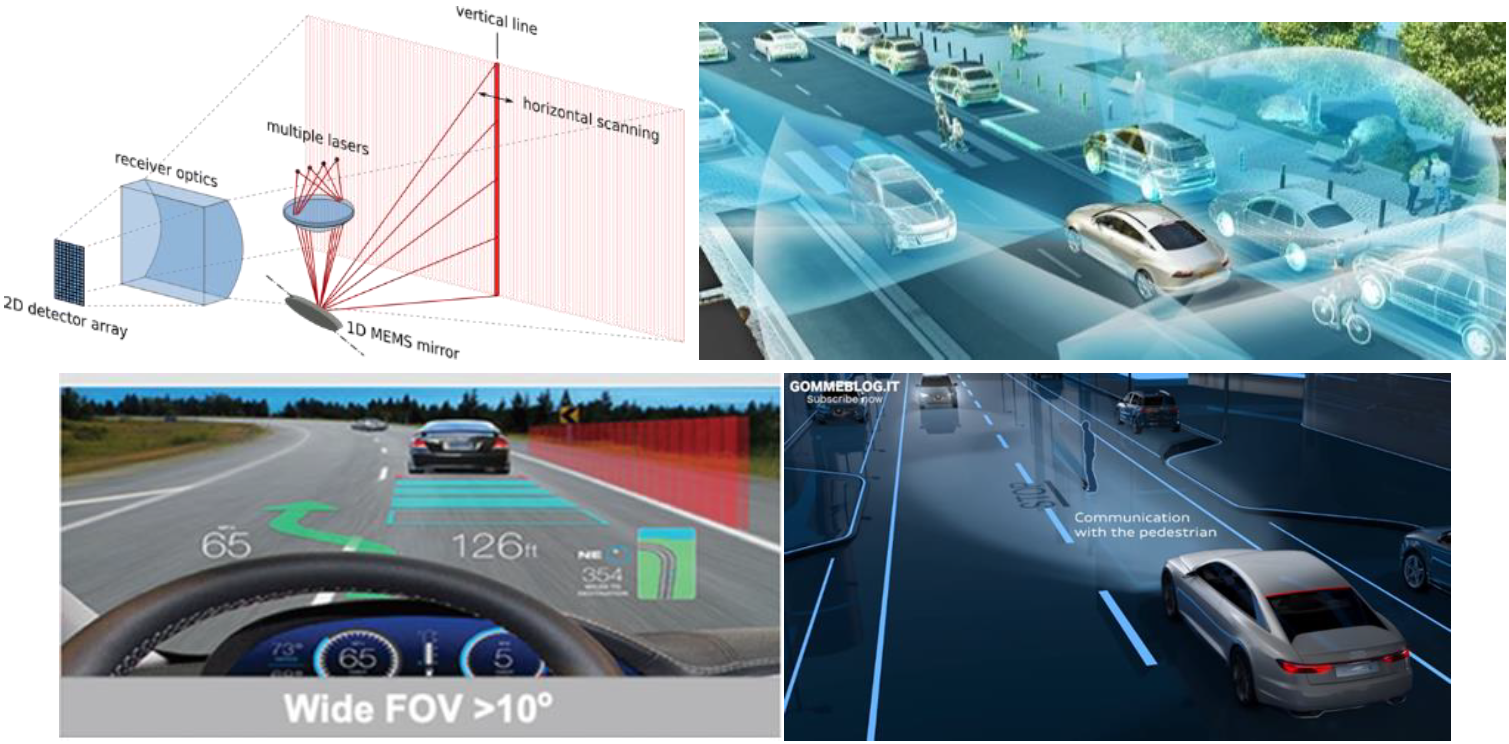
Concepts of (top left) 1D MEMS scanning lidar [Yoo et al, E & I, 135, 6, 2018], (top right) lidars and other sensors for surroundings [Hecht, Optics Photonics News, 29, 1, 2018], (bottom left) AR head up display [Ballard et al, SID DTP, 2016], and (bottom right) smart headlights [Audi OLED | Audi Future LAB, 2015, link
Applications
- Lidar for autonomous driving
- Augmented reality head up display
- Precision measurement systems
Related Publications and Patents
Journal articles
- R. Schroedter, H. W. Yoo, D. Brunner, and G. Schitter, Charge-Based Capacitive Self-Sensing With Continuous State Observation for Resonant Electrostatic MEMS Mirrors, Journal Of Microelectromechanical Systems, vol. 30, iss. 6, p. 897–906, 2021.
[BibTex] [Download]@article{TUW-299022, author = {Schroedter, Richard and Yoo, Han Woong and Brunner, David and Schitter, Georg}, title = {Charge-Based Capacitive Self-Sensing With Continuous State Observation for Resonant Electrostatic MEMS Mirrors}, journal = {Journal Of Microelectromechanical Systems}, year = {2021}, volume = {30}, number = {6}, pages = {897--906}, doi = {10.1109/JMEMS.2021.3107797}, keywords = {Charge-based capacitive self-sensing , resonant MEMS mirror , electrostatic comb drive , switched current integrator , capacitance network , nonlinear switched input Luenberger observer} }
- D. Brunner, H. W. Yoo, R. Schroedter, and G. Schitter, Adaptive Lissajous scanning pattern design by phase modulation, Optics Express, vol. 29, iss. 18, p. 27989–28004, 2021.
[BibTex] [Download]@article{TUW-296868, author = {Brunner, David and Yoo, Han Woong and Schroedter, Richard and Schitter, Georg}, title = {Adaptive Lissajous scanning pattern design by phase modulation}, journal = {Optics Express}, year = {2021}, volume = {29}, number = {18}, pages = {27989--28004}, doi = {10.1364/OE.430171} }
- H. W. Yoo, D. Brunner, M. Macho, L. Niedermueller, A. J. Devesa, L. Kormann, and G. Schitter, Evaluation of robustness against external vibrations for long-range MEMS lidar with one-dimensional resonant micromirror, Journal of Optical Microsystems, vol. 2, iss. 1, 2022.
[BibTex] [Download]@article{TUW-303700, author = {Yoo, Han Woong and Brunner, David and Macho, Matthias and Niedermueller, Leonhard and Devesa, Angel Jurado and Kormann, Leonhard and Schitter, Georg}, title = {Evaluation of robustness against external vibrations for long-range MEMS lidar with one-dimensional resonant micromirror}, journal = {Journal of Optical Microsystems}, year = {2022}, volume = {2}, number = {1}, doi = {10.1117/1.JOM.2.1.011007}, keywords = {Microelectromechanical systems, LIDAR, Mirrors, Clouds, Receivers, Transmitters, Field programmable gate arrays, Optical microsystems, Video, Microcontrollers} }
News
Project partners
Funding
- FFG Mobilität der Zukunft
This project (activity) has received funding from the Mobility of the Future programme. Mobility of the Future is a research, technology and innovation funding programme of the Republic of Austria, Ministry of Climate Action. The Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG) has been authorised for the programme management
Ansprechpartner
Univ.-Prof. Dipl.-Ing. Dr.sc.techn. Georg SchitterDr. MSc Han Woong Yoo
ProjektmitarbeiterInnen
Dr. MSc Han Woong YooDipl.-Ing. Dr.-Ing. Richard Schroedter
Dipl.-Ing. BSc. David Brunner