
SpecTrackular2024 - 2027
This project aims to develop an optical telescope system capable of spectroscopic analysis of space debris. In order to achieve the high-precision telescope pointing and tracking required for this application, a self-learning pointing model and an improvement of orbit prediction based on obtained data will be developed. Ultimately, spectroscopic analysis can give information on the material, pose and rotation of space debris. Read more →
Versatile technology platform for MEMS scan system for automotive safety applications (AUTOScan)2021 - 2024
Advancements of sensors, communication and artificial intelligence are about to bring a revolutionary changes in mobility and transportation by autonomous driving. Scanning mirrors based on Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) technologies are one of the promising solutions for various automotive applications, e.g. photonic sensing such as lidars and human machine interfaces such as augmented reality head -up display (AR HUD) and smart headlights. The AUTOScan project aims for automotive grade MEMS scanning systems for robust sensing and imaging in harsh automotive environmental conditions, enabling reliable MEMS lidars and AR HUDs. Read more →
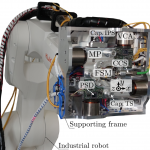
Precision robotic in-line metrology for freeform surfaces
High precision in-line measurements on free form surfaces are considered as a key factor for future industrial production. Robot-based measurement systems enable the required flexibility but are typically lacking the required precision. The scope of this project is the development of a measurement platform as end effector for a robot robot arm, carrying a measurement tool and compensating for environmental disturbances, enabling precision inline measurements. Read more →

Hybrid reluctance actuators for high precision motion
Next-generation high-quality motion systems require high-precision actuators with higher energy efficiency and larger force to improve the system throughput. Particularly, actuators with a motor constant higher than comparable voice coil actuators are highly desired. This project investigates hybrid reluctance actuators (HRAs) with guiding flexures as a promising candidate of next-generation systems. Read more →
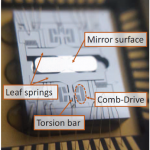
High resolution long range Lidar for autonomous driving (LiDcAR)2017 - 2020
Lidar is an acronym for light detection and ranging, in analogy to radar. Lidar has received much attention in the automotive industry as a key component for high level automated driving systems. Compared to other sensing techniques such as stereo cameras and radar, lidar can provide high resolution and highly accurate 3D measurements of the surroundings and robust detection in various weather conditions. Read more →

TracSat
The precise tracking of high velocity satellites with ground based optical telescopes is a prerequisite for a number of future applications such as optical satellite communication, observation of space debris or satellite laser ranging. To achieve this goal, good mechatronic design as well as high performance control are necessary. Together with our industrial partner, ASA Astrosysteme GmbH, this project aims on increasing the achievable precision and tracking velocity of existing ASA ground stations. Read more →

Fundamentals of opto-mechatronic systems (OMC)
Currently innovation is taking place at the border of disciplines rather than in one individual field of engineering. This particularly holds for application domains that span more than one field of engineering, since a high level of system integration from different disciplines provides solutions that a single domain alone cannot provide. As an example, the combination of optics and mechatronics form the interdisciplinary field of opto-mechatronics. Read more →

Characterization of highly divergent optics (DOC)
Opto-mechatronic devices such as triangulation sensors or polychromatic confocal sensors project focused light beams onto the surface of the measuring object. Assessing the properties of the focused beam is essential as they are directly related to the achievable measurement resolution and precision of the opto-mechatronic device. Read more →

Atomic Force Microscopy capable of vibration isolation (Vibrostop AFM)
An atomic force microscope (AFM) can image and inspect a sample surface with high resolution by scanning a probe with a sharp tip over the sample. During scanning, the vertical position of the probe with respect to the sample typically needs to be regulated with nanometer resolution. For the required high resolution, AFMs are sensitive to vibrations transmitted from the floor dependent on their design. Read more →

Automated in-line metrology for nanopositioning systems (aim4np)
Within the scope of this project, a novel approach is developed for robot-based in-line metrology to isolate nanoscale measurements from environmental vibrations. Instead of isolating sample and robot from floor vibrations by means of passive or active vibration isolation aids, the distance between sample and metrology tool is kept constant. Read more →