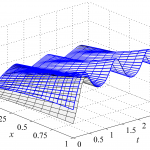
Backstepping-based observer design for parabolic PDEs with varying parameters
Model-based control and advanced process monitoring usually require full state information. This is in particular evident if control strategies are utilized by means of state feedback or if algorithms based on full state knowledge are applied to improve the insight into the system behavior, e.g., for diagnostic or error detection purposes. In general, the complete state information cannot be directly measured. This is especially true for distributed-parameter systems, i.e., systems governed by partial differential equations (PDEs).Therefore, an observer is required to estimate the state variables from the knowledge of measured input and output variables as well as the mathematical model of the system. Read more →

Flatness control in heavy plate rolling
In heavy plate rolling, the heated plates are plastically deformed between two work rolls. Here, asymmetries in the roll gap may cause up- or downward bending of the ends of the plates. This so-called ski effect affects the flatness of the plates and may entail problems in subsequent processing steps. A model-based control concept and an improved speed controller for the roll drives can avoid such ski-ends and thus increase the quality of the plates. Read more →

Modeling and control of hot levelers
Levelers are used in the production of steel plates in rollings mills to improve the flatness of the products. After rolling and cooling, a leveling machine reduces remaining flatness errors and residual stresses in the plates. This happens by alternate plastic bending of the plate material between the work rolls of the leveler. Read more →

Modeling, observer design, control, and optimization of strip annealing furnaces
In the steel industry, continuous strip annealing furnaces are used for the heat treatment of strip products. To meet the high demands on the quality of the final product, the strip has to be heated to a predefined target temperature while it moves through the furnace. This is a challenging control task because an annealing furnace is a complex, nonlinear, thermodynamical multi-input-multi-output system and many process variables cannot be measured. Read more →

Modeling and control of a four-high heavy plate rolling mill
In heavy plate rolling, the heated plate is plastically deformed between two work rolls. Various measures avoid or minimize the deflection of the work rolls and thus the lateral non-uniformity of the product thickness profile. A mathematical deflection model yields the plate exit thickness, which cannot be directly measured. A model-based feedforward strategy compensates the disturbances observed in the previous rolling pass. Read more →

Lateral guiding and shape control in heavy plate rolling
In the rolling process of heavy plates, contour errors (deviations from the desired straight contour in the top view) and a lateral off-center position of the plate in the rolling mill may occur. Tailored continuum-mechanics models explain the reasons for these errors. The errors are monitored in real time by a camera-based measurement system. Model-based control strategies ensure that contour errors are avoided and that the plate moves straight through the rolling mill. Read more →

Modeling, observer design, and control of continuous slab reheating furnaces
In the steel industry, products are reheated in continuous reheating furnaces as a preparation for rolling. The reheating process requires large amounts of energy and incurs high costs. The temperature during this process is decisive for the product quality. Based on mathematical process models, state observers and controllers for the non-measureable product temperature are developed. The nonlinear model-predictive multi-input multi-output controller ensures a high accuracy, minimized energy consumption, and reduced CO2-emissions of the reheating process. Read more →
MMAssist II2017 - 2020
The goal of the project partners in MMAssist II is to research and implement modular, reusable assistance systems for employees in production companies. For that, the project partners will work on the exemplary uses cases Maintenance and Service, Arming of Machines and Simultaneous Handling of Multiple Machines, and Montage to analyze the technical and sozio-economic requirements for assistance systems in these areas. Read more →
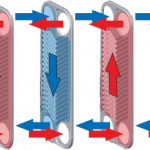
Modeling and Control of a Cooling System with compact plate heat exchangers2010 - 2014
Fluid-fluid cooling systems are widely used in industrial applications. The mathematical model of a heat exchanger is a distributed-parameter system because of the convective heat transfer. The parametrization of the heat transfer requires extensive identintification. Thus, a nonlinear control law was designed in this project, which is indepent of the overall heat transfer coefficient. Read more →

Soft landing strategies for electromagnetic fast-switching valves
This project is concerned with the development of a soft landing control strategy electromagnetic valves. The main goal is to guarantee time-optimal switching of the valves with minimal impact velocity of the plunger at the limit stops. Thus, the approach combines the benefits of fast response and low maintenance intervals. Read more →